Uterine fibroids
Fibroids are muscular tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus. Fibroids can grow as a single tumor, or there can be many of them in the uterus. The size of the fibroids may varies from very small size to big size.
About 20 percent to 80 percent of women develop fibroids by the time they reach age 50. Some women with fibroids do not have any symptoms. Some have pain and heavy menstrual bleeding. Fibroids also can put pressure on the bladder, causing frequent urination, or the rectum, causing rectal pressure. Fibroids can also present as a pelvic mass when they get very large.
Fibroids can be categorized into:
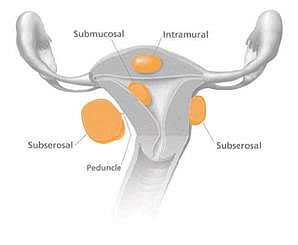
- Submucosal fibroids grow into the uterine cavity.
- Intramural fibroids grow within the wall of the uterus.
- Subserosal fibroids grow on the outside of the uterus.
- Pedunculated fibroids grow on stalks that grow out from the surface of the uterus or into the cavity of the uterus.
Usually a pelvic ultrasound can confirm whether you have fibroids. Sometimes other imaging tests, e.g. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used.
Depending on your symptoms, you may be treated by medications or surgery:
- Medications
- If you have heavy bleeding during your period, medications will be prescribed to reduce your menstrual flow and iron supplement may be prescribed if you have anaemia.
- Analgesia can be used for mild pain.
- Medications containing hormone (oral medications or injections) can be prescribed to help control symptoms of fibroids.
- Surgery
If you have fibroids with moderate or severe symptoms, surgery may be the best way to treat them. Here are the options:- Myomectomy – surgery to remove fibroids without taking out the healthy tissue of the uterus.
- Hysterectomy – surgery to remove the uterus
- Endometrial ablation – the lining of the uterus is destroyed to control very heavy bleeding
- Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE) – Tiny plastic or gel particles are injected into the blood vessels that supply blood to the fibroid. This blocks the blood supply to the fibroid, causing it to shrink.
Please consult your doctor to formulate the best treatment option for you.



